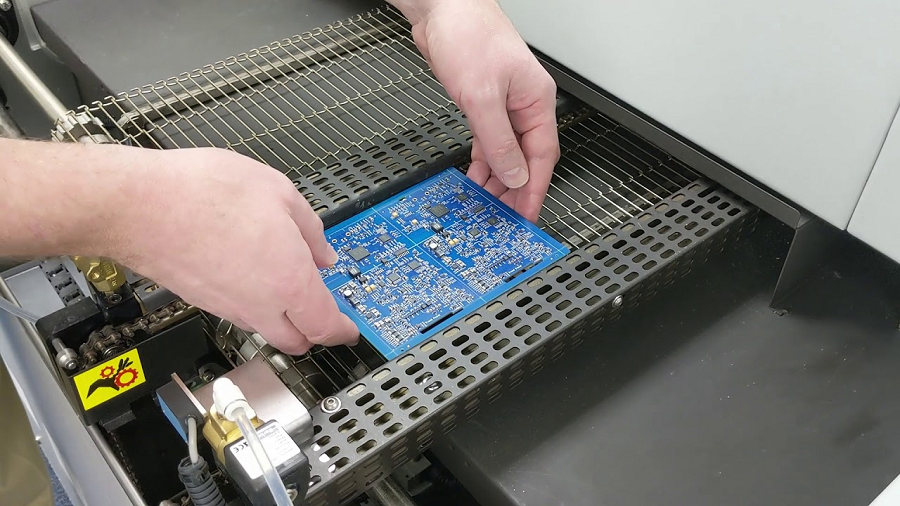
Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) has been a cornerstone of the electronics industry for decades. As technology continues to advance at an unprecedented pace, the methods and materials used in PCBA have also evolved, reflecting the growing demands for smaller, faster, and more efficient electronic devices. In 2024, several key trends and innovations are shaping the future of PCBA, driving the industry toward even greater levels of performance and reliability.
The Rise of Miniaturization
One of the most significant trends in PCBA is the ongoing push toward miniaturization. As electronic devices become increasingly compact, the components within these devices must also shrink. This trend is especially evident in consumer electronics, such as smartphones, wearables, and IoT devices, where space is at a premium. To accommodate the need for smaller components, manufacturers are adopting advanced techniques like surface-mount technology (SMT), which allows for the placement of tiny components directly onto the surface of a PCB. This approach not only saves space but also enhances the performance of the device by reducing signal loss and improving electrical connections.
In addition to SMT, another innovation driving miniaturization is the use of high-density interconnect (HDI) technology. HDI PCBs feature finer lines and spaces, smaller vias, and more densely packed components, enabling manufacturers to fit more functionality into a smaller footprint. This is crucial for industries such as telecommunications, where the demand for high-performance devices in compact forms continues to grow.
Automation and Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
As the complexity of PCBs increases, so does the need for precision and efficiency in the assembly process. In 2024, automation is playing a pivotal role in revolutionizing PCBA. Automated assembly lines equipped with advanced robotics and AI-driven systems are now commonplace, significantly reducing the potential for human error and increasing production speeds.
One of the key benefits of automation in PCBA is the ability to achieve consistent quality across large production runs. With automated systems, manufacturers can maintain tight tolerances and ensure that every PCB meets stringent quality standards. This is particularly important in industries such as aerospace and medical devices, where even the smallest defect can have serious consequences.
Furthermore, advanced manufacturing techniques such as 3D printing are beginning to make their mark on the PCBA industry. While still in the early stages of adoption, 3D printing offers the potential to create complex, multi-layered PCBs with intricate geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve using traditional methods. As this technology matures, it could open up new possibilities for custom and low-volume PCB production.
The Impact of IoT and 5G on PCBA
The proliferation of the Internet of Things (IoT) and the rollout of 5G networks are two major forces driving innovation in PCBA. IoT devices, which range from smart home appliances to industrial sensors, require PCBs that are not only small and efficient but also capable of handling wireless communication and data processing. As a result, PCBA processes must accommodate the integration of radio frequency (RF) components, antennas, and other specialized features.
Similarly, the deployment of 5G networks is placing new demands on PCB design and assembly. 5G technology requires PCBs that can operate at higher frequencies and handle greater data loads than previous generations of wireless technology. This has led to the development of new materials, such as low-loss laminates and advanced soldering techniques, which can improve signal integrity and reduce interference in 5G-enabled devices.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
As environmental concerns become increasingly prominent, the PCBA industry is also evolving to address sustainability. In 2024, there is a growing emphasis on reducing the environmental impact of PCB manufacturing and assembly. This includes the use of lead-free solder, the recycling of materials, and the implementation of energy-efficient production processes.
One area where sustainability is making a significant impact is in the development of biodegradable and recyclable PCBs. Researchers are exploring the use of organic materials, such as cellulose and plant-based resins, to create PCBs that can break down naturally at the end of their lifecycle. While still in the experimental phase, these innovations have the potential to reduce the electronic waste generated by discarded devices, contributing to a more sustainable future.
The Importance of Turn-Key Solutions
In response to the increasing complexity of PCBA, many companies are turning to turn-key printed circuit board assembly solutions. These services offer a one-stop-shop approach, where a single provider handles every aspect of the PCBA process, from design and component sourcing to assembly and testing. This not only simplifies the supply chain but also ensures that all elements of the PCB are perfectly coordinated, leading to faster production times and higher-quality outcomes.
Turn-key solutions are particularly valuable for companies looking to bring new products to market quickly. By partnering with a single provider, they can streamline the development process, reduce lead times, and focus on their core competencies while leaving the technical details to the experts. As a result, turn-key PCBA is becoming an increasingly popular choice for manufacturers across a wide range of industries.
Conclusion
The evolution of Printed Circuit Board Assembly in 2024 is marked by significant advancements in miniaturization, automation, and sustainability. As the demands for smaller, faster, and more efficient electronic devices continue to grow, the PCBA industry is responding with innovative technologies and processes that push the boundaries of what is possible. From the rise of 3D printing to the adoption of turn-key solutions, these trends are shaping the future of PCBA and setting the stage for the next generation of electronic devices.